Difference between revisions of "Annotating the Wall"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
*I. [[Jones polynomial]] for right trefoil knot; [https://theportal.wiki/wiki/Jones_polynomial Witten’s path-integral formulation] for Jones polynomial using Chern-Simons action | *I. [[Jones polynomial]] for right trefoil knot; [https://theportal.wiki/wiki/Jones_polynomial Witten’s path-integral formulation] for Jones polynomial using Chern-Simons action | ||
*II. [[ | *II. [[Feynman Diagram]] illustrating [[Associativity]] equation in [[Quantum Field Theory]] | ||
*III. [[Yang-Baxter equation]] | *III. [[Yang-Baxter equation]] | ||
*IV. [[Lorenz Attractor]]: Lorenz equations with orbit | *IV. [[Lorenz Attractor]]: Lorenz equations with orbit | ||
*V. Diagram of a black hole with [[Schwarzschild radius]] | *V. Diagram of a black hole with [[Schwarzschild radius]] | ||
*VI. The five [[ | *VI. The five [[Regular Polyhedra]] | ||
*VII. Equiangular spiral drawn in "golden" rectangle (side ratio = golden mean g), ratio of consecutive [[Fibonacci numbers]] approaches g, represented by its continued fraction expansion. | *VII. Equiangular spiral drawn in "golden" rectangle (side ratio = golden mean g), ratio of consecutive [[Fibonacci numbers]] approaches g, represented by its continued fraction expansion. | ||
*VIII.[[Babylonian computation of the square root of 2]] | *VIII.[[Babylonian computation of the square root of 2]] | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
*X. [[Cell decomposition of torus; Euler characteristic; Gauss-Bonnet formula.]] | *X. [[Cell decomposition of torus; Euler characteristic; Gauss-Bonnet formula.]] | ||
*XI. Archimedes: [[On the Sphere and Cylinder]]. | *XI. Archimedes: [[On the Sphere and Cylinder]]. | ||
*XII. [[Aharanov-Bohm | *XII. [[Aharanov-Bohm Effect]] | ||
*XIII.[[Supergravity Langangian]]; root diagramm for [[Lie | *XIII.[[Supergravity Langangian]]; root diagramm for [[Lie Group E8]] | ||
*XIV. [[Navier-Stokes equation]] with flow around cylinder. | *XIV. [[Navier-Stokes equation]] with flow around cylinder. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
*E. [[Heisenberg's indeterminacy relation]] | *E. [[Heisenberg's indeterminacy relation]] | ||
*F. [[Euler's formula for Zeta-function]] | *F. [[Euler's formula for Zeta-function]] | ||
*G. Interaction between two string; [[Feynman | *G. Interaction between two string; [[Feynman Diagram]] shows corresponding interaction of particles, here the Compton scattering of a photon off an electron. | ||
Revision as of 20:27, 4 February 2021
- A High Resolution Interactive Version of the Wall has been created
The following list contains the names of all equations, formulas, and illustrations that are shown on the Wall. The goal is to create a helpful explanation for each element of the list.
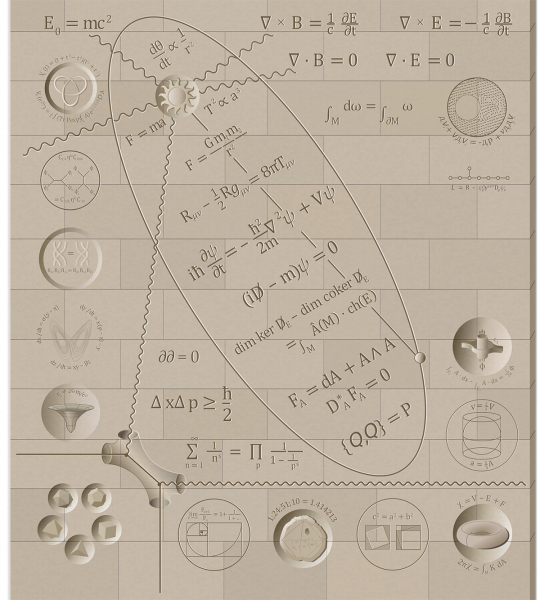
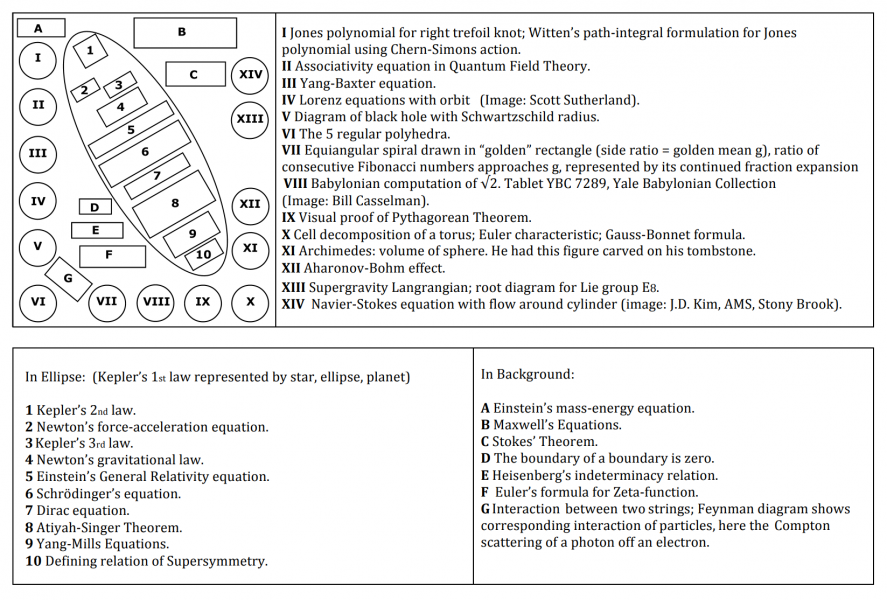
- I. Jones polynomial for right trefoil knot; Witten’s path-integral formulation for Jones polynomial using Chern-Simons action
- II. Feynman Diagram illustrating Associativity equation in Quantum Field Theory
- III. Yang-Baxter equation
- IV. Lorenz Attractor: Lorenz equations with orbit
- V. Diagram of a black hole with Schwarzschild radius
- VI. The five Regular Polyhedra
- VII. Equiangular spiral drawn in "golden" rectangle (side ratio = golden mean g), ratio of consecutive Fibonacci numbers approaches g, represented by its continued fraction expansion.
- VIII.Babylonian computation of the square root of 2
- IX. Visual proof of the Pythagorean Theorem
- X. Cell decomposition of torus; Euler characteristic; Gauss-Bonnet formula.
- XI. Archimedes: On the Sphere and Cylinder.
- XII. Aharanov-Bohm Effect
- XIII.Supergravity Langangian; root diagramm for Lie Group E8
- XIV. Navier-Stokes equation with flow around cylinder.
- 0. In Ellipse: (Kepler's 1st law represented by star, ellipse, planet)
- 1. Kepler's 2nd law
- 2. Newton's force-acceleration equation
- 3. Kepler's 3rd law
- 4. Newton's gravitational law
- 5. Einstein's General Relativity equation
- 6. Schrödinger's equation
- 7. Dirac equation
- 8. Atiyah-Singer Theorem
- 9. Yang-Mills equations
- 10. Defining relation of Supersymmetry
- A. Einstein’s mass-energy equation
- B. Maxwell's Equations
- C. Stoke's Theorem
- D. The boundary of a boundary is zero
- E. Heisenberg's indeterminacy relation
- F. Euler's formula for Zeta-function
- G. Interaction between two string; Feynman Diagram shows corresponding interaction of particles, here the Compton scattering of a photon off an electron.